Wealth distribution is a powerful force that shapes the socioeconomic fabric of nations. The distribution of resources, income, and opportunities within a society plays a pivotal role in determining the quality of life, social mobility, and overall economic health.
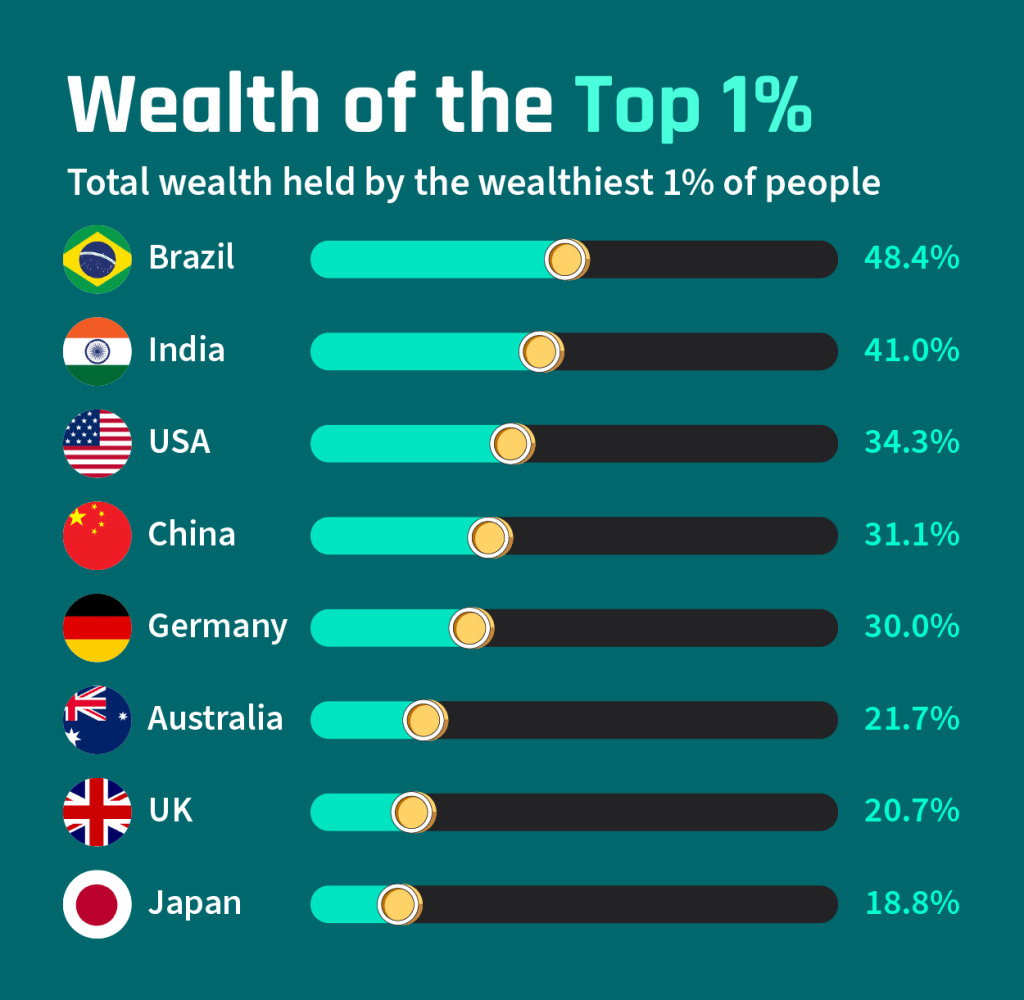
In this blog, we’ll embark on a comparative journey between two starkly different models of wealth distribution, examining the contrasting landscapes of India and the Scandinavian countries.
Unequal Wealth Distribution in India
India, with its rich cultural diversity and a burgeoning economy, also grapples with significant wealth inequality. A sizable portion of the population faces economic hardships, while a select few amass substantial wealth. The factors contributing to this imbalance are multifaceted:
- Historical Disparities: Historical legacies, such as the caste system, have left enduring imprints on India’s social structure. This has translated into economic disparities, with certain communities facing systemic obstacles that hinder wealth accumulation.
- Urban-Rural Divide: India’s rapid urbanization has created a stark divide between urban and rural areas. Urban centers often experience concentrated wealth and economic opportunities, leaving rural regions with limited access to resources and economic growth.
- Limited Social Safety Nets: The absence of robust social safety nets further exacerbates wealth inequality. Limited access to quality education, healthcare, and social services hinders upward mobility for a significant portion of the population.
- Gender Disparities: Gender inequalities persist in India, affecting women’s access to education, employment, and financial independence. These disparities contribute to an uneven distribution of wealth within the society.
Scandinavia: A Model of Better Wealth Distribution
Contrastingly, the Scandinavian countries – Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland, and Iceland – stand out for their more equitable wealth distribution. These nations consistently rank high on global indices measuring social equality, and several factors contribute to this commendable scenario:
- Social Welfare Systems: Scandinavia boasts robust social welfare systems that prioritize universal access to education, healthcare, and other essential services. This ensures that the benefits of economic growth are widely shared among the population.
- Progressive Taxation: Progressive taxation is a cornerstone of the Scandinavian economic model. High-income individuals and corporations face higher tax rates, contributing to a more equitable distribution of resources.
- Strong Labor Unions: The presence of strong labor unions empowers workers to negotiate fair wages and working conditions. This collective bargaining power helps reduce income disparities and fosters a more inclusive economic environment.
- Investment in Education: Extensive investments in education at all levels contribute to a skilled and adaptable workforce. This, in turn, promotes social mobility and reduces the perpetuation of wealth within specific elite circles.
Comparative Analysis
The contrasting experiences of India and Scandinavia highlight the profound impact of wealth distribution on various aspects of society:
- Quality of Life: In Scandinavia, where wealth is more evenly distributed, citizens generally enjoy a higher quality of life. Access to healthcare, education, and social services contributes to overall well-being. In contrast, India’s unequal wealth distribution contributes to disparities in living standards and access to basic amenities.
- Social Mobility: The Scandinavian model facilitates greater social mobility, allowing individuals to move beyond their socio-economic backgrounds. In India, the entrenched disparities often hinder upward mobility, perpetuating economic inequalities across generations.
- Economic Stability: A more equitable distribution of wealth contributes to economic stability in Scandinavia. The middle class plays a crucial role in driving economic growth, fostering a resilient economy. In India, wealth concentration among a few can contribute to economic volatility and social unrest.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: While both India and Scandinavia have vibrant entrepreneurial ecosystems, the more egalitarian societies of Scandinavia encourage a broader range of individuals to participate in innovation and business ventures. In India, economic disparities may limit entrepreneurial opportunities for a significant portion of the population.
Way Forward
Wealth distribution emerges as a defining factor in shaping the destinies of nations. The stark differences between India and Scandinavia underscore the importance of policies and societal structures in fostering economic equality. As India strives for inclusive growth, there is much to learn from the Scandinavian model. Implementing policies that address historical disparities, bridge urban-rural divides, and promote social safety nets could pave the way for a more equitable and prosperous India. In the global pursuit of sustainable development, the lessons drawn from diverse models of wealth distribution can serve as guiding beacons toward a more just and balanced economic future.

